
Cryptocurrency markets never sleep, nor do the bots that trade them.
In fact, algorithmic trading has come to dominate much of the crypto market – automated bots now manage nearly three-quarters of all crypto trading volume and provide approximately 84% of market liquidity.
For experienced crypto traders, this reality conveys a clear message: to remain competitive, you must leverage automated trading. However, possessing a crypto trading bot is not a magic bullet by itself. Success depends on the strategies you program these bots to implement.
What advanced cryptocurrency trading strategies can help you outsmart the market and capture profits around the clock?
This comprehensive guide explores a variety of proven tactics – from trend-following algorithms and arbitrage systems to market-making and AI-driven strategies. We’ll skip the basics for beginners and concentrate on actionable insights and detailed examples that experienced traders will value.
Are you ready to uncover the best ways to use a crypto automated trading bot in real market conditions? Let’s dive in and enhance your approach to algorithmic crypto trading.
Trend-Following Bot Strategies
When the market is trending strongly, going with the flow can be very profitable. Trend-following strategies allow your bot to ride sustained price moves by automatically entering trades in the direction of the trend and staying in as long as the momentum lasts.
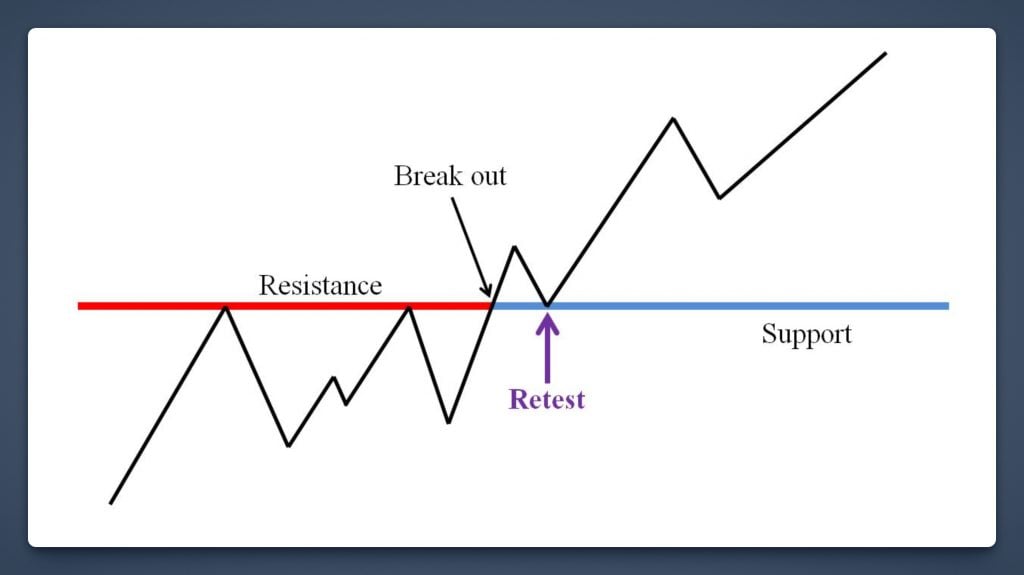
The core idea is straightforward: “the trend is your friend. ” Instead of fighting the market’s direction, a trend bot identifies when a cryptocurrency’s price is breaking out upward or downward and jumps on for the ride.
One common approach is momentum breakout trading.
For example, you might program your bot to buy Bitcoin when it breaks above a key resistance level or a recent high, confirming an uptrend. The bot could utilize technical indicators like moving average crossovers or the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to gauge momentum.
Suppose Bitcoin has been consolidating around $30,000 and then surges to $31,500 on high volume – a trend-following bot can identify this breakout and open a long position immediately, much faster than a human could react. As the price continues to rise, the bot remains in the trade.
Trailing stop-losses are frequently paired with trend bots to secure gains. The bot dynamically adjusts the stop-loss price upward as the market rises (or downward for shorts) to safeguard profits if the trend reverses. For example, if our bot purchased BTC at $31,500 and the price climbs to $34,000, a trailing stop might increase to $33,000. If the trend weakens and the price falls, the bot exits at $33,000, capturing a significant portion of the profit. In a strong trend, however, the bot never hits the stop – it continuously recalibrates the stop level as the market rises, allowing winners to run.
Advanced trend-following bots can employ multiple time-frame analysis or filter out false signals.
An experienced trader might program the bot to only trade breakouts that align across daily and hourly charts, or require confirmation from volume and volatility indicators (like the Average True Range) before executing trades.
This approach helps avoid being whipsawed by short-lived price spikes. The goal is to enable the bot to participate in major directional moves without being misled by every small fluctuation.
Actionable tip: Keep an eye on when the market shifts to a choppy, sideways range – during these times, a trend bot should either stand aside or switch to a different strategy. Many advanced traders maintain a toolkit of strategies and activate the trend-following bot only when conditions are favorable. By aligning your crypto bot with the prevailing trend and using effective safeguards, you ensure it capitalizes on significant moves while managing risk when the trend eventually concludes.
Mean Reversion and Range Trading Bots
Not all markets are trending; often, crypto prices fluctuate within a range or repeatedly return to an average value. Mean reversion strategies aim to exploit these fluctuations by buying low and selling high, based on the assumption that extreme moves will revert to the mean.
In simpler terms, when a coin’s price dips sharply, a mean-reversion bot sees a potential bargain and buys, anticipating a rebound. Conversely, when the price spikes up swiftly, the bot sells or short-sells, expecting a pullback.
A popular application of mean reversion in cryptocurrency is the grid trading bot.
Grid bots create a predefined price range and place a series of buy and sell orders at set intervals (the “grid”) within that range. For instance, if Ethereum has been fluctuating between $1,800 and $2,200 for weeks, a grid bot could establish this band as its trading range. It might place buy orders every $50 down from $2,000 (for example, $1,950, $1,900, $1,850, etc.) and sell orders every $50 up from $2,000 ($2,050, $2,100, $2,150, etc.).
Whenever Ethereum’s price dips, the bot accumulates at the lower grid levels; when the price swings back up, the bot sells at the higher grid levels, capturing profit on each swing. The advantage of a grid strategy is that it systematically “buys the dip and sells the rip” in a choppy market without requiring any predictive forecasting.
Learn more: Crypto swing trading
Mean reversion bots often use technical indicators like Bollinger Bands or RSI to signal overbought or oversold conditions. For example, an experienced trader might configure a bot to buy when RSI falls below 30 (oversold) and sell when RSI rises above 70 (overbought), assuming prices will revert after reaching those extreme levels.
Similarly, Bollinger Bands (which plot standard deviations around a moving average) can prompt a bot to act when the price touches the lower band (potentially undervalued) or the upper band (potentially overvalued).
However, mean reversion can be risky if a genuine trend emerges. A bot that continuously buys a declining asset in anticipation of a rebound may accumulate a losing position if the asset continues to drop.
Effective risk management is crucial. Implementing stop-loss levels for mean reversion trades is essential – for instance, the bot might limit losses if Ethereum falls 10% below the lowest point of the grid range, recognizing that the range has been breached. Likewise, position sizing should be cautious, as mean reversion trades can move against you longer than anticipated.
Learn more: Crypto trading risk management
To maximize effectiveness, mean reversion strategies should be used in markets that show clear range-bound behavior or statistical mean reversion. Identifying such conditions may involve analyzing historical volatility and price distribution.
Many advanced traders activate their mean reversion or grid bots during quiet consolidation phases and deactivate them when a breakout (and thus a new trend) appears to be forming.
Essentially, the key is to align the bot with the market environment – employing range-trading bots when the market is range-bound and switching them off (or altering strategy) when the market starts trending in one direction.
Arbitrage Bots: Exploiting Price Differences
Cryptocurrency markets are fragmented across numerous exchanges, which means that at any given moment, the price of a coin can vary slightly from one exchange to another. Arbitrage trading bots exploit these price discrepancies by buying on the cheaper market and simultaneously selling on the more expensive one.
The objective is to secure a virtually risk-free profit before the prices converge. While simple in concept, arbitrage in practice is a sophisticated strategy that requires speed, precision, and careful execution.
Before diving into examples, it’s crucial to highlight that arbitrage opportunities in crypto are often fleeting – they can disappear in seconds or even faster. Successful arbitrage bots operate with minimal latency and may even be co-located on exchange servers to achieve maximum speed.
They also must account for trading fees, withdrawal fees, and slippage; a price difference isn’t truly profitable if fees consume the spread or if the act of trading alters the price.
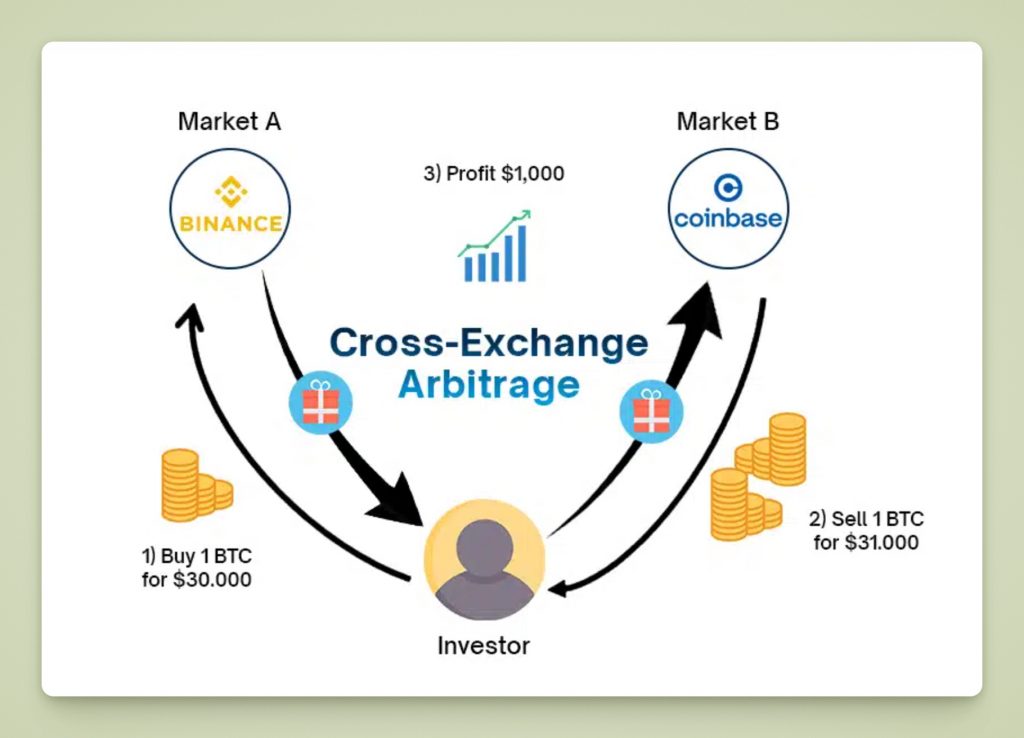
Cross-Exchange Arbitrage
The most straightforward arbitrage bot strategy is cross-exchange arbitrage. In this strategy, the bot scans multiple exchanges for a coin trading at varying prices.
For instance, suppose Exchange A lists Bitcoin at $30,100 while Exchange B lists it at $30,200. An arbitrage bot connected to both exchanges can instantly buy BTC on Exchange A and sell the same amount of BTC on Exchange B, securing a profit of $100 per BTC price difference (minus fees).
To execute this, the bot needs capital readily available on both exchanges. It buys with funds from Exchange A and sells using an equivalent amount of BTC that is pre-funded on Exchange B. All of this must occur nearly simultaneously to prevent market movements from closing the price gap. If executed correctly, the bot achieves a profit in the form of extra dollars on Exchange B and additional BTC on Exchange A (which can later be equalized).
A key challenge here is moving funds between exchanges. Often, arbitrage bots avoid actual transfers during trades by maintaining inventory on each exchange (as in the example above).
Transferring cryptocurrency across exchanges is too slow and can eliminate the opportunity. Instead, advanced arbitrageurs periodically rebalance their holdings between exchanges outside of trading hours to ensure that each exchange has sufficient capital for the next round of trades. It’s a capital-intensive approach, but necessary for serious cross-market arbitrage.
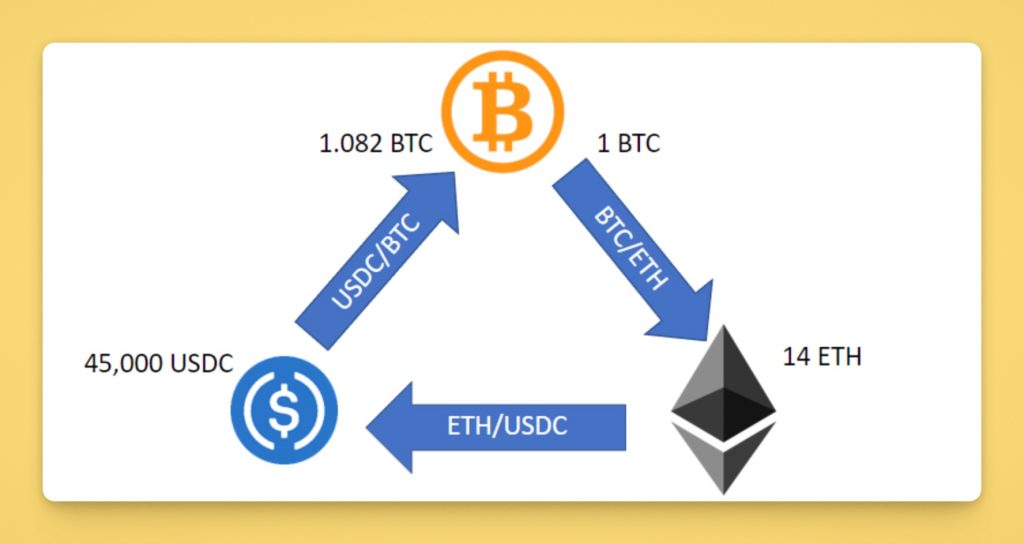
Triangular Arbitrage
Another sophisticated variant is triangular arbitrage, which occurs on a single exchange but involves three trading pairs. In the realm of crypto, this often entails exploiting price discrepancies among three currencies that form a triangular relationship of exchange rates.
For instance, suppose on Exchange X there’s a discrepancy between the trading pairs of Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and a stablecoin such as USDT A triangular arbitrage bot might observe that the price of ETH in terms of BTC, when combined with the price of BTC in terms of USDT, does not align with the direct price of ETH in USDT.
Specifically, the bot could execute three sequential trades within seconds: sell USDT to acquire BTC, then use that BTC to purchase ETH, and finally sell the ETH back to USDT.
If the relative exchange rates are misaligned, this sequence results in obtaining more USDT than it started with. Since all trades occur on the same exchange, there are no withdrawal times to worry about; however, the bot must operate at exceptional speed to complete the cycle before the market adjusts.
Triangular arbitrage opportunities are typically very short-lived, and the profit per cycle may be minimal (fractions of a percent). However, a high-frequency bot can repeat these cycles numerous times, and with sufficient volume, those small profits accumulate.
Advanced bots also consider trading fees for each leg of the triangle and will only execute if the net outcome is positive after fees are taken into account.
Decentralized (DEX) Arbitrage
In the era of decentralized finance, arbitrage bots have also entered the DeFi space. Decentralized exchanges like Uniswap and PancakeSwap frequently exhibit price discrepancies compared to centralized exchanges and other DEXs.
For instance, a DEX arbitrage bot might detect that a token is priced lower on Uniswap than on Binance. The bot can purchase from Uniswap (via an Ethereum transaction) and sell on Binance at a higher price. Alternatively, it may engage in arbitrage between two DEXs if the liquidity pools of one have become misaligned with those of another.
DEX arbitrage presents its own challenges: executing trades on-chain involves managing network transaction fees and blockchain latency. On Ethereum, high gas fees can rapidly diminish arbitrage profits.
Additionally, there’s a risk of transaction failure – if the price fluctuates before your transaction is mined, the trade may fail or even result in a loss. Some bots utilize flash loans (borrowing large amounts of crypto within a single transaction) to enhance arbitrage on DEXs without requiring substantial capital, but this approach is highly advanced.
DEX arbitrage bots often have to operate directly on smart contracts and compete with other bots in the mempool, resulting in a specialized arms race of its own.
Risks and Considerations for Arbitrage Bots
Arbitrage is often regarded as “risk-free,” but in reality, there are execution risks. Slippage can occur if the buying or selling process changes the price. If your bot isn’t the fastest, a competing bot may seize the opportunity first, leaving you with an open trade at an unfavorable price.
This situation is known as being “legged” – for example, you buy on one exchange but fail to sell in time on the other before the price equalizes, effectively buying high without an offsetting sell.
To mitigate this, some arbitrage bots set very strict conditions: they won’t execute unless the price gap is well above a minimum threshold (to accommodate fees and slippage), and they monitor order book depth to assess whether their trade will impact the price.
Moreover, markets can occasionally move in unison due to significant news or crashes, negating what initially appeared as an arbitrage opportunity. Always test your arbitrage bot in real-time with small amounts before scaling up. This will uncover practical issues such as network delays or exchange API limits.
Additionally, consider concentrating on pairs and exchanges where you observe consistent small divergences – these are your bot’s ideal targets. Arbitrage can be highly profitable for a well-tuned system, but it’s a competitive field that requires ongoing monitoring and adjustments to maintain an edge.
Market-Making and High-Frequency Strategies
While arbitrage seeks to exploit price differences, market-making bots aim to profit by consistently providing liquidity. A market-making bot places limit orders on both the buy and sell sides of the order book, earning the spread (the difference between bid and ask prices) through numerous trades.
Essentially, the bot seeks to “buy low and sell high” in a very short-term context – for example, buying at $100.00 and selling at $100.10 repeatedly. Market makers thrive on volume and tight spreads, often realizing small profits on each trade that accumulate over thousands of cycles.
An effective market-making strategy might involve posting orders just inside the current best bid and best ask. For instance, if Ether is quoted at $1,995 bid / $2,000 ask, the bot could place a buy order at $1,996 and a sell order at $1,999.
When another trader’s order fills the bot’s sell at $1,999, the bot earns $3 (minus fees) because it bought earlier at $1,996. Similarly, if someone sells into the bot’s $1,996 bid, the bot will then try to sell that Ether at $1,999 or higher. By continuously updating orders as the market moves, the bot maintains a presence on both sides of the order book.
One challenge in market making is inventory management. If the price suddenly trends in one direction, the bot could end up holding too much of one side (e.g., accumulating a large amount of Ether if the price continues to fall and it’s buying the dips). Advanced market-making bots use algorithms to adjust or withdraw quotes during periods of high volatility to avoid being “run over” by significant price movements.
They might also implement an inventory risk limit – for instance, if the bot’s Ether inventory surpasses a certain threshold due to excessive buying, it temporarily halts further buy orders or widens the spread to decrease additional purchases.
High-frequency trading (HFT) techniques often go hand-in-hand with market making. These bots operate on extremely short time frames, sometimes holding positions for mere seconds or less.
Latency is critical; being mere milliseconds faster than competitors can lead to your orders being filled first. Some advanced high-frequency trading (HFT) bots in cryptocurrency even monitor order book depth and microstructure signals, attempting to predict immediate price movements (such as an order imbalance indicating that the price will rise) and position themselves accordingly.
This goes beyond traditional market making into the realm of algorithmic scalping, where the bot seeks to capture quick profits from any small fluctuations it detects.
Learn More: Algorithmic crypto trading
It’s important to note that high-frequency market-making strategies are technically demanding. They require stable, low-latency connections, and often direct market access through exchange APIs or co-located servers.
For individual traders, competing with professional HFT firms can be challenging, but crypto markets are relatively less efficient than traditional markets, leaving room for well-crafted bots to carve out niche opportunities.
Actionable tip: If you operate a market-making bot, pay close attention to exchange fee structures. Many exchanges offer rebates on maker fees or lower fees for providing liquidity. Utilizing a platform or account type that rewards market makers can transform a marginal strategy into a profitable one.
Additionally, always implement safeguards – a sudden news event can cause prices to gap, so your bot should be equipped to cancel outstanding orders quickly (or you should have a “kill switch” script ready) to avoid significant unintended losses.
By diligently managing these factors, market-making bots can consistently accumulate gains even in relatively stable markets.
AI-Powered and Adaptive Trading Bots
With the rise of artificial intelligence in trading, some crypto bots now incorporate machine learning algorithms and other AI techniques to adapt to market patterns. These AI-driven trading bots move beyond static rule sets and strive to learn from data or adjust their strategies based on changing conditions.
For experienced traders, this represents an opportunity to develop even more resilient automated strategies, although it brings additional complexity.
One example of an AI-driven strategy involves using a machine learning model to predict short-term price direction. A trader might train a neural network on historical price and volume data (as well as alternative data such as social media sentiment) to forecast the probability of the price going up or down within the next hour.
The bot then executes trades based on the model’s output – for instance, if the model indicates an 80% chance that Bitcoin’s price will rise in the next hour, the bot might initiate a long position, potentially with a tight stop in case the prediction is incorrect.
Over time, the model can be retrained with new data to enhance its accuracy, allowing the bot’s strategy to adapt. Some advanced bots even utilize reinforcement learning, learning by trial and error in simulations to determine profitable strategies independently.
Another AI approach involves sentiment analysis and news feeds. These bots utilize natural language processing to gauge market sentiment from sources such as Twitter, Reddit, or news headlines.
For instance, if an AI bot identifies a sudden surge of positive sentiment regarding Ethereum (perhaps due to a viral partnership announcement), it could buy ETH moments before the price potentially increases, getting in ahead of slower human traders.
Conversely, detecting negative sentiment or anomalies in on-chain data may prompt the bot to reduce exposure or short certain assets. This strategy blurs the line between technical and fundamental analysis by leveraging real-time information that extends beyond price charts.
While AI-driven strategies may sound enticing, they are not a guaranteed shortcut to profits. Machine learning models can overfit to past data, performing well in backtests but failing in live markets when conditions change.
There is also a “black box” element; unlike a simple moving average crossover, where you know exactly what triggers a trade, a neural network’s decision-making can be opaque. This opacity means troubleshooting a losing streak can be difficult, as you may not understand why the bot is making certain trades.
For these reasons, experienced traders using AI bots often keep a human involved. They might leverage AI for signal generation while still applying human judgment or additional filters before executing large trades.
Rigorous out-of-sample testing and walk-forward analysis are essential when developing AI-based strategies to ensure they generalize beyond the training period. Furthermore, even an AI bot requires robust risk management rules – if a model begins to perform poorly, the bot should reduce trade size or halt trading until it is retrained.
In summary, AI and machine learning can enhance crypto bot trading strategies by uncovering hidden patterns and reacting to news at lightning speed. However, they work best as an additional tool in the trader’s toolkit, complementing traditional strategies instead of completely replacing them.
The most effective automated trading bot setups may combine rule-based methods with a touch of AI insight, all while ensuring the overall system remains understandable and manageable.
Risk Management and Optimization
Regardless of how sophisticated your crypto bot trading strategies may be, risk management remains the cornerstone of long-term success. An automated strategy can quickly generate profits, but it can also amplify losses just as rapidly if left unmonitored. Experienced traders understand that every algorithmic strategy must include built-in safeguards and ongoing optimization.
Position sizing is a critical element. Just because a bot can execute trades 24/7 doesn’t mean you should risk more per trade. Many professionals use formulas like the Kelly criterion or a fixed percentage risk model (for instance, risking no more than 1-2% of the account on any single trade).
This approach ensures that no single bad trade (or series of trades) can wipe out your capital. With bots, this is especially important – a rapid sequence of losing trades could occur while you’re not watching, so the bot’s trade size should be calibrated to withstand a streak of losses.
Another key safeguard is to set stop-loss and take-profit levels that align with the strategy. We’ve mentioned trailing stops for trend-following bots and stop thresholds for mean-reversion bots. In practice, you should program your bot with clear exit criteria for every position it takes.
For instance, a bot implementing a momentum strategy might automatically exit if the trade moves 5% against it, while a scalping bot might cut losses after a 0.2% drop. The take-profit could be based on technical targets or simply mirror the entry trigger in reverse (e.g., if a bot bought because the RSI was low, it might sell once the RSI rises).
Drawdown control is another essential aspect of risk management. This involves monitoring the peak-to-valley equity decline in your bot’s performance. Advanced trading bots can be programmed to stop trading or reduce position size if the drawdown exceeds a specific threshold (for example, 10% of account equity).
This type of circuit breaker prevents a runaway strategy from depleting your account during unfavorable market conditions or as a result of a flawed algorithm update. It provides you with an opportunity to intervene, assess what went wrong, and adjust the strategy before resuming operations.
Regular performance reviews and optimizations are essential for maintaining a strategy’s profitability over the long term. Market conditions change – what worked brilliantly in last year’s bull market may struggle in a sideways or bear market.
As an experienced trader, you should periodically reassess your bot’s trade log and key metrics. Evaluate win rate, average win versus average loss, maximum consecutive losses, and more. If you notice a decline in performance, it’s time to fine-tune the parameters or even replace the strategy with a new one. This might involve adjusting indicator thresholds, retraining an AI model with updated data, or improving the bot’s timing (for example, by adding a slight delay to avoid false breakouts).
Backtesting and forward testing are invaluable. Always test your bot on historical data to assess how the strategy would have performed in various past market scenarios. Then, conduct a forward test in a paper trading environment or with a small live allocation to ensure it behaves as expected in real time. A strategy that succeeds in both backtesting and forward testing with favorable results and manageable risk is a strong candidate for scaling up.
Finally, remember that automation doesn’t imply a set-and-forget approach. Even the best bot for crypto trading requires human oversight. Treat your trading bots as skilled assistants – they can manage the heavy lifting of execution, but you, as the “manager,” need to oversee their results and intervene when necessary.
By implementing strict risk management rules and continuously optimizing your strategies, you’ll keep your automated trading on track and safeguard your capital through market ups and downs.
Scaling Up with Crypto Prop Firms
At some point, you may find that your strategies are performing well, but you’re constrained by your own capital or risk tolerance. This is where partnering with a crypto proprietary trading firm can be a game-changer for algorithmic traders.
Best crypto prop firms offer traders access to larger capital accounts in exchange for a share of the profits. Essentially, if you can demonstrate that your trading strategies are profitable, a crypto prop firm will provide funding, allowing you to trade, for instance, a $100,000 account instead of just your personal $5,000.
The upside is evident: your bot’s 5% monthly return on $5k (which is $250) could escalate to $5,000 on a $100k account – all while you still only risk the firm’s capital.
Not all prop firms are equal, especially in crypto and automated trading. Many traditional setups focus on Forex or stocks and require proprietary software. In contrast, HyroTrader caters to digital asset traders, allowing bot usage on real crypto exchanges.
For example, it connects your trading bot via API to a funded exchange account. This ensures your algorithm trades in a real market with actual liquidity, not simulations. The key benefit is real-market integration, enabling genuine performance of your crypto strategies on exchange order books (like Bybit), avoiding distortions from fake feeds or proxy platforms.
Prop firms like HyroTrader offer significant benefits, including a profit split of up to 70-90%, covering losses beyond your drawdown limit. They provide clear risk management rules (e.g., maximum daily drawdown, restrictions on illiquid coins) while allowing flexibility in trading strategies like arbitrage, trend-following, or high-frequency scalping. With a solid bot that adheres to these parameters, you can trade larger amounts without risking more personal capital.
The community and resources at HyroTrader are notable. On the HyroTrader reviews page, traders share how they advanced their careers using firm capital. These testimonials emphasize the advantages of daily payouts and reduced exchange-related risks, as the firm manages security and accounts. This automated trading approach allows you to concentrate on strategy while the firm handles back-end operations, promptly paying out profits in stablecoins.
Is a prop firm right for you?
If you’re confident in your bot strategies and have a track record, consider a prop firm evaluation. Firms usually assess your skills through a crypto demo trading account, where you must meet a specific profit target with controlled risk. After passing, you get a funded account. This instills good risk discipline, complementing the systematic discipline your bot provides.
In summary, scaling with a crypto prop firm amplifies returns and provides professional infrastructure. More algo traders are exploring this path. HyroTrader, a leading firm, offers real exchange connectivity and generous profit-sharing, designed by crypto traders for traders.
Increased capital demands extra vigilance with risk; a bot managing $100k needs careful oversight just like your own funds. Combine your proven strategy with the firm’s support for impactful automated trading.
Conclusion
Crypto bot trading offers many strategies for experienced traders. It’s crucial to deploy the right strategy at the right time: trend-following bots for major trends, mean reversion bots for range-bound markets, arbitrage bots for steady gains from inefficiencies, and AI bots that adapt to data. Adding strong risk management helps protect your capital.
Automation boosts trading efficiency, but your strategy and oversight ensure bots remain profitable. As crypto markets evolve, it is crucial to stay informed and adaptable. Refine your trading strategies, utilize prop firm funding when ready to scale, and continue learning from market cycles. With a solid combination of strategy, technology, and discipline, you can effectively navigate the crypto landscape.